The Impact of GIS and Remote Sensing on Environmental Monitoring
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing (RS) technologies have become indispensable tools in environmental monitoring and management. These technologies enable researchers and policymakers to analyze and visualize environmental data with unprecedented accuracy and detail. In this blog, we explore the significant impacts of GIS and RS on environmental monitoring.
Understanding GIS and Remote Sensing
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing spatial and geographic data. It allows users to visualize, question, and interpret data to understand relationships, patterns, and trends. GIS technology is widely used in various fields, including urban planning, disaster management, and natural resource management.
Remote Sensing (RS)
Remote sensing involves the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with it. This is typically done via satellite or aerial imagery. Remote sensing technologies provide critical data for monitoring changes in the environment, such as deforestation, urbanization, and climate change.
Benefits of GIS and Remote Sensing in Environmental Monitoring
Enhanced Data Collection and Analysis
GIS and remote sensing technologies provide accurate and up-to-date data, which is crucial for effective environmental monitoring. These technologies enable the collection of data over large and inaccessible areas, providing a comprehensive view of the environment.
Example:
Using satellite imagery, researchers can monitor the health of forests and detect illegal logging activities. This data can then be analyzed using GIS to identify patterns and predict future deforestation hotspots.

Improved Decision Making
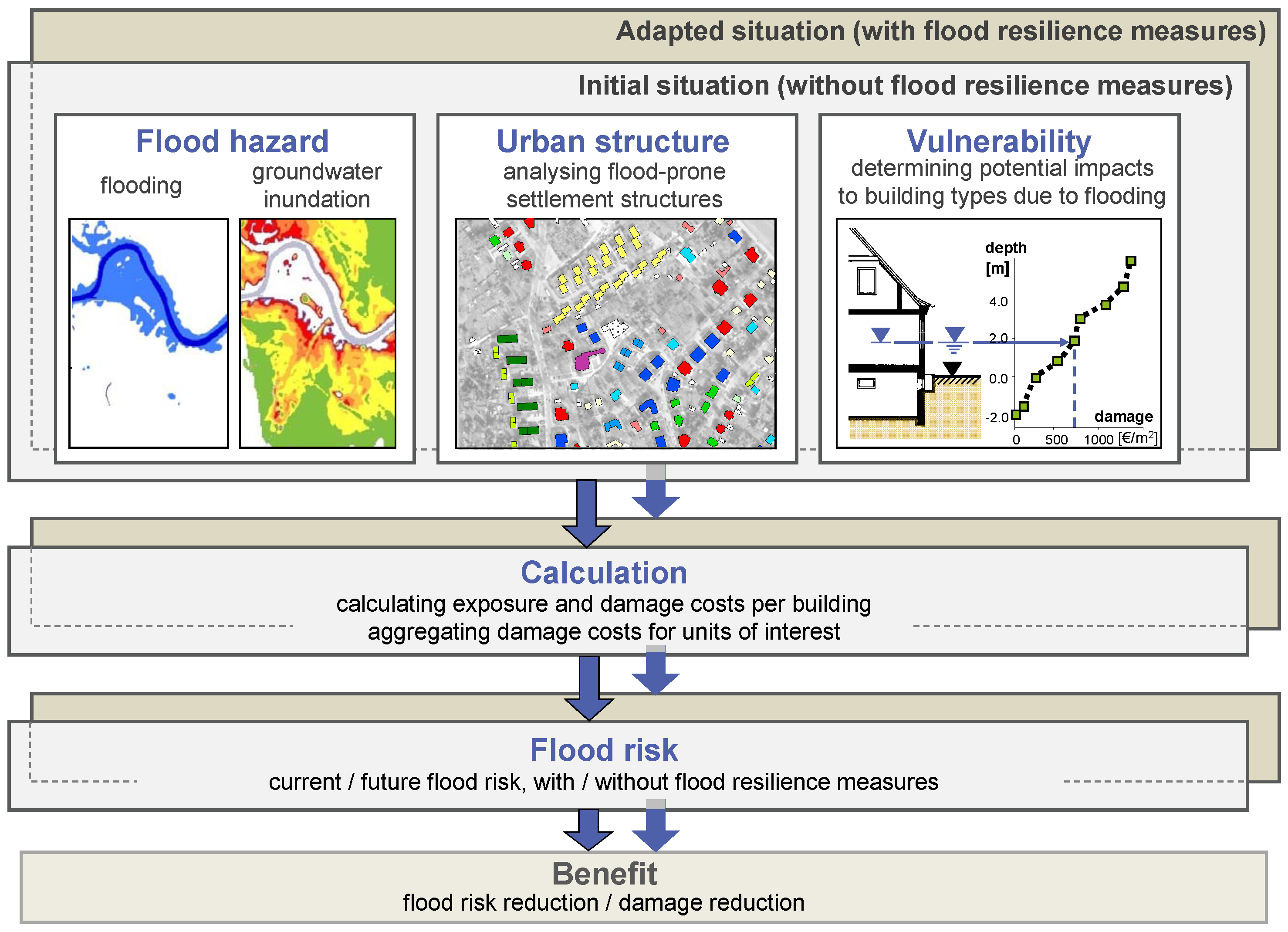
The ability to visualize and analyze environmental data in GIS allows policymakers to make informed decisions. By integrating various data sources, GIS provides a holistic view of environmental issues, enabling better planning and management.
Example:
GIS can be used to model the impact of natural disasters, such as floods and hurricanes, helping authorities to develop effective response strategies and mitigate risks.
Cost-Effective Monitoring
Remote sensing technologies reduce the need for costly and time-consuming field surveys. Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide a cost-effective means of monitoring large areas over time, making it possible to track environmental changes with high frequency.
Example:
Monitoring agricultural lands using remote sensing helps in assessing crop health, estimating yields, and identifying areas affected by pests or diseases, thereby optimizing resource allocation.
Challenges and Limitations
Data Accuracy and Resolution
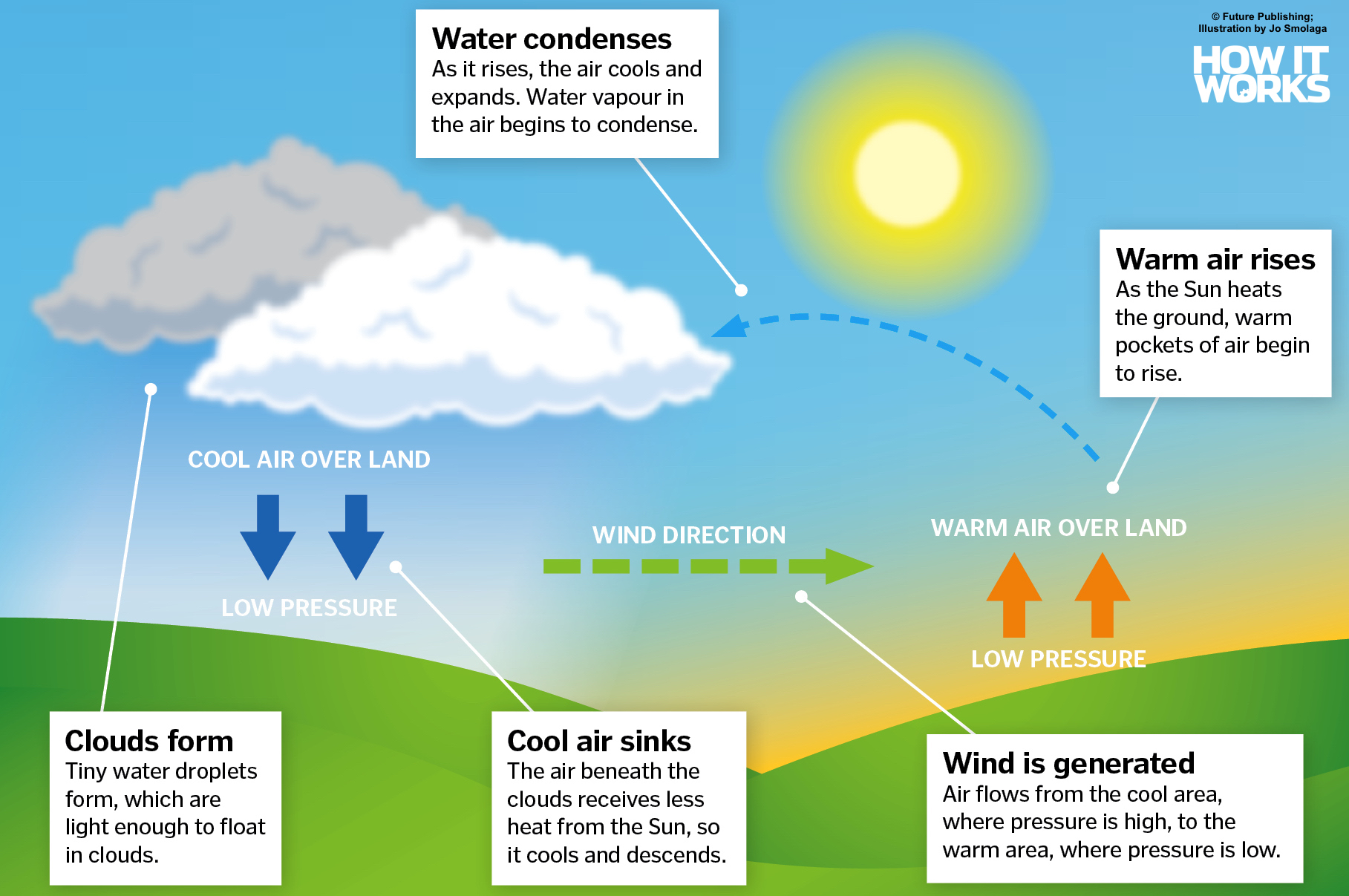
While GIS and remote sensing provide valuable data, the accuracy and resolution of this data can sometimes be a limitation. Factors such as cloud cover, atmospheric conditions, and sensor limitations can affect the quality of remote sensing data.
Technical Expertise
Effective use of GIS and remote sensing technologies requires specialized technical expertise. There is a need for skilled professionals who can interpret and analyze the data accurately.
Data Integration
Integrating data from various sources can be challenging. Different data sets may have varying formats, scales, and resolutions, making it difficult to create a cohesive analysis.
Future Outlook
The future of GIS and remote sensing in environmental monitoring looks promising, with advancements in technology continually improving data accuracy and analysis capabilities. Emerging technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence are further enhancing the potential of GIS and remote sensing.
Innovations on the Horizon
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are being developed to analyze remote sensing data more efficiently, identifying patterns and anomalies with greater accuracy.
-
Drones: The use of drones for environmental monitoring is increasing, providing high-resolution imagery and real-time data collection.
-
Climate Modeling: Improved climate models are being integrated with GIS to predict and mitigate the impacts of climate change more effectively.
Conclusion
GIS and remote sensing technologies are revolutionizing environmental monitoring, providing accurate, timely, and cost-effective data for decision-making. As technology continues to advance, the potential for these tools to address environmental challenges will only grow. Embracing these innovations is crucial for sustainable environmental management and conservation efforts.
References
- FlexJobs, "The Benefits of Remote Work," 2023. Read more
- Stanford University, "Remote Work and Productivity," 2023. Read more
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), "GIS and Remote Sensing," 2022. Read more
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), "Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring," 2023. Read more
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), "Using GIS for Environmental Conservation," 2023. Read more
Visual Aids
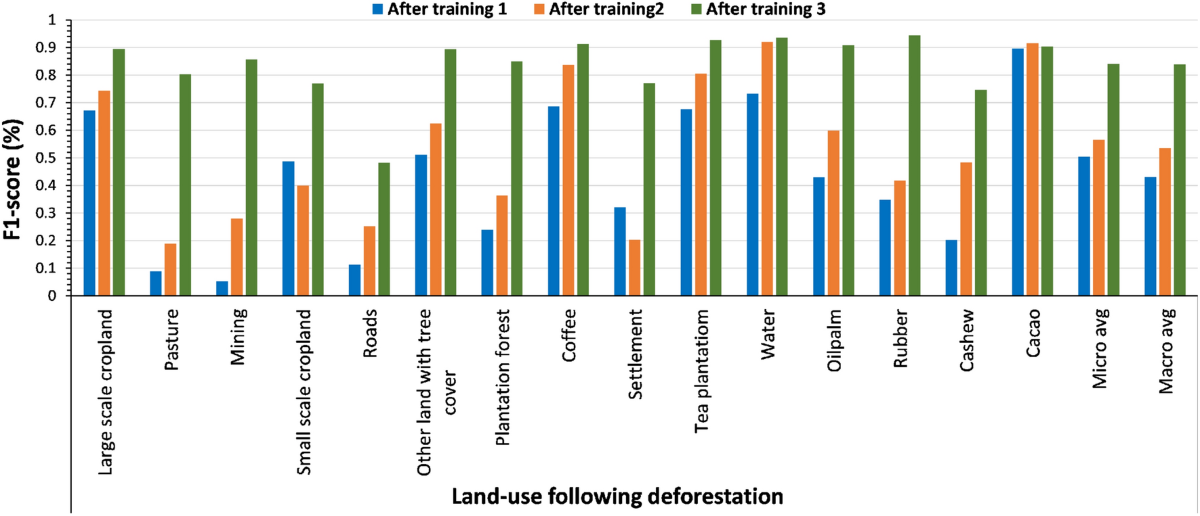
Deforestation Monitoring
Climate Change Impact
